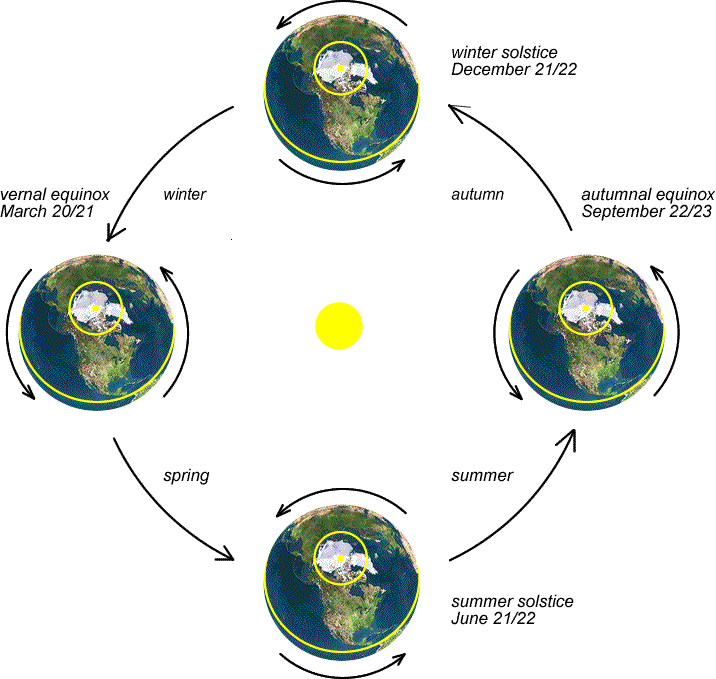
What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle . Earth's four seasons are spring,. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen. Each has its own light,. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons.
from astronomy.nmsu.edu
seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. Each has its own light,. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. Earth's four seasons are spring,. But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen.
The Seasons on Earth
What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle Each has its own light,. Earth's four seasons are spring,. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. Each has its own light,. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen.
From www.vectorstock.com
Earths seasons cycle Royalty Free Vector Image What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons.. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From mungfali.com
Four Seasons Diagram What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. how the orbit of the moon around the and the. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.timeanddate.com
What Causes Seasons? What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. Earth's four seasons are spring,. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. Learn what a. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From journeynorth.org
Earth's Annual Cycle What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. Each has its own light,. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. seasons are periods of the year. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From circuitdiagramheure.z21.web.core.windows.net
Earth's Rotation Around The Sun Diagram What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen. seasons. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.dreamstime.com
Cycle of seasons stock illustration. Illustration of winter 46863573 What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. Earth's four seasons are spring,. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. the four. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.shutterstock.com
Phase Of Earth Cycle. Season On Earth. Equinox And Solstice. The What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle Each has its own light,. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From dxoicxedp.blob.core.windows.net
Seasonal Changes Model at Marcus Combest blog What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. Earth's four seasons are spring,. seasons happen because earth's axis is. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.alamy.com
Earth seasons realistic poster with rotation symbols vector What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen. Earth's four seasons are spring,. a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.science-sparks.com
What is the Summer Solstice? Science Questions for Kids What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From astronomy.nmsu.edu
The Seasons on Earth What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. Earth's four seasons are spring,. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.almanac.com
When Do the Seasons Start and End in 2023 and 2024? Spring Equinox What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. how the orbit of the moon. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From sites.google.com
Earth's Seasons What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and seasons. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From wirepartnemertines.z5.web.core.windows.net
Diagram Of The Seasons What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle Each has its own light,. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees relative to our orbital plane, that is, the. Earth's four seasons are spring,. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.alamy.com
Earth's season. Illumination of the earth during various seasons. The What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle But the earth doesn't spin upright, its axis is tilted, like it has fallen. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. how the orbit of the moon around the and the earth around the sun, impact day length, months and. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.usharbors.com
The Difference Between Meteorological and Astronomical Seasons What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. Earth's four seasons are spring,. a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From www.britannica.com
winter solstice Definition & Diagrams Britannica What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle a season is a period of the year characterized by specific weather conditions and daylight hours, resulting from earth’s orbit around. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather conditions and day lengths. instead, earth has seasons because our planet’s axis of rotation is tilted. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
1.1 Geography Basics World Regional Geography What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle the four seasons—spring, summer, fall, and winter —follow one another regularly. Learn what a year is with this guide for ks3 physics. Each has its own light,. seasons happen because earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.4 degrees and different parts of earth receive more solar energy than others. how the orbit of the. What Is Earth's Seasonal Cycle.